Most objects can be reduced broadly into three tone masses, the lights (including the high lights), the half tones, and the shadows. And the habit of reducing things into a simple equation of three tones as a foundation on which to build complex appearances should early be sought for.
Exercise in Mass Drawing.
Here is a simple exercise in mass drawing with the brush that is, as far as I know, never offered to the young student. select a simple object: some of those casts of fruit hanging up that are common in art schools will do. Place it in a strong light and shade, preferably by artificial light, as it is not so subtle, and therefore easier; the 111light coming from either the right or left hand, but not from in front. Try and arrange it so that the tone of the ground of your cast comes about equal to the half tones in the relief.

Plate XXIII.
SET OF FOUR PHOTOGRAPHS OF THE SAME PAINTING FROM A CAST IN DIFFERENT STAGES
No. 1. Blocking out the shape of spaces to be occupied by masses.
No. 2. A middle tone having been scumbled over the whole, the lights are now painted. Their shapes and the play of lost-and-foundness on their edges being observed. Gradations are got by thinner paint, which is mixed with the wet middle tone of the ground, and is darkened

Plate XXIV.
SET OF FOUR PHOTOGRAPHS OF THE SAME PAINTING FROM A CAST IN DIFFERENT STAGES
No. 3. The same as the last, with the addition of the darks; variety being got in the same way as in the case of the lights, only here the thinner part is lighter, whereas in the case of the lights it was darker.
No. 4. The finished work, refinements being added and mistakes corrected.
First draw in the outlines of the masses strongly in charcoal, noting the shapes of the shadows carefully, taking great care that you get their shapes blocked out in square lines in true proportion relative to each other, and troubling about little else. Let this be a setting out of the ground upon which you will afterwards express the form, rather than a drawing—the same scaffolding, in fact, that you were advised to do in the case of a line drawing, only, in that case, the drawing proper was to be done with a point, and in this case the drawing proper is to be done with a brush full of paint. Fix the charcoal well with a spray diffuser and the usual solution of white shellac in spirits of wine.
Taking raw umber and white (oil paint), mix up a tone that you think equal to the half tones of the cast before you. Extreme care should be taken in matching this tone. Now scumble this with a big brush equally over the whole canvas (or whatever you are making your study on). Don't use much medium, but if it is too stiff to go on thinly enough, put a little oil with it, but no turpentine. By scumbling is meant rubbing the colour into the canvas, working the brush from side to side rapidly, and laying just the thinnest solid tone that will cover the surface. If this is properly done, and your drawing was well fixed, you will just be able to see it through the paint. Now mix up a tone equal to the highest lights on the cast, and map out simply the shapes of the light masses on your study, leaving the 112scumbled tone for the half tones. Note carefully where the light masses come sharply against the half tones and where they merge softly into them.
You will find that the scumbled tone of your ground will mix with the tone of the lights with which you are painting, and darken it somewhat. This will enable you to get the amount of variety you want in the tone of the lights. The thicker you paint the lighter will be the tone, while the thinner paint will be more affected by the original half tone, and will consequently be darker. When this is done, mix up a tone equal to the darkest shadow, and proceed to map out the shadows in the same way as you did the lights; noting carefully where they come sharply against the half tone and where they are lost. In the case of the shadows the thicker you paint the darker will be the tone; and the thinner, the lighter.
When the lights and shadows have been mapped out, if this has been done with any accuracy, your work should be well advanced. And it now remains to correct and refine it here and there, as you feel it wants it. Place your work alongside the cast, and walk back to correct it. Faults that are not apparent when close, are easily seen at a little distance.
I don't suggest that this is the right or only way of painting, but I do suggest that exercises of this description will teach the student many of the rudimentary essentials of painting, such elementary things as how to lay a tone, how to manage a brush, how to resolve appearances into a simple structure of tones, and how to manipulate your paint so as to express the desired shape. This elementary paint drawing is, as far as I know, never 113given as an exercise, the study of drawing at present being confined to paper and charcoal or chalk mediums. Drawing in charcoal is the nearest thing to this "paint drawing," it being a sort of mixed method, half line and half mass drawing. But although allied to painting, it is a very different thing from expressing form with paint, and no substitute for some elementary exercise with the brush. The use of charcoal to the neglect of line drawing often gets the student into a sloppy manner of work, and is not so good a training to the eye and hand in clear, definite statement. Its popularity is no doubt due to the fact that you can get much effect with little knowledge. Although this painting into a middle tone is not by any means the only method of painting, I do feel that it is the best method for studying form expression with the brush.
But, when you come to colour, the fact of the opaque middle tone (or half tone) being first painted over the whole will spoil the clearness and transparency of your shadows, and may also interfere with the brilliancy of the colour in the lights. When colour comes to be considered it may be necessary to adopt many expedients that it is as well not to trouble too much about until a further stage is reached. But there is no necessity for the half tone to be painted over the shadows. In working in colour the half tone or middle tone of the lights can be made, and a middle tone of the shadows, and these two first painted separately, the edges where they come together being carefully studied and finished. Afterwards the variety of tone in the lights and the shadows can be added. By this means the difference in the quality of the colour between 114lights and shadows is preserved. This is an important consideration, as there is generally a strong contrast between them, the shadows usually being warm if the lights are cool and vice versa; and such contrasts greatly affect the vitality of colouring.
Try always to do as much as possible with one stroke of the brush; paint has a vitality when the touches are deft, that much handling and continual touching kills. Look carefully at the shape and variety of the tone you wish to express, and try and manipulate the swing of your brush in such a way as to get in one touch as near the quality of shape and gradation you want. Remember that the lightest part of your touch will be where the brush first touches the canvas when you are painting lights into a middle tone; and that as the amount of paint in the brush gets less, so the tone will be more affected by what you are painting into, and get darker. And in painting the shadows, the darkest part of your stroke will be where the brush first touches the canvas; and it will gradually lighten as the paint in your brush gets less and therefore more affected by the tone you are painting into. If your brush is very full it will not be influenced nearly so much. And if one wants a touch that shall be distinct, as would be the case in painting the shiny light on a glazed pot, a very full brush would be used. But generally speaking, get your effects with as little paint as possible. Thinner paint is easier to refine and manipulate. There will be no fear of its not being solid if you are painting into a solidly scumbled middle tone.
Many charming things are to be done with a mixture of solid and transparent paint, but it is 115well at first not to complicate the problem too much, and therefore to leave this until later on, when you are competent to attack problems of colour. Keep your early work both in monochrome and colour quite solid, but as thin as you can, reserving thicker paint for those occasions when you wish to put a touch that shall not be influenced by what you are painting into.
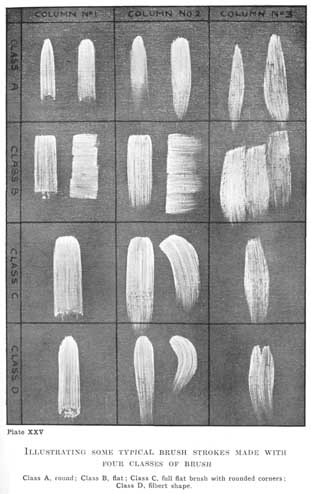
Plate XXV.
ILLUSTRATING SOME TYPICAL BRUSH STROKES MADE WITH FOUR CLASSES OF BRUSH
Class A, round; Class B, flat; Class C, full flat brush with rounded corners; Class D, filbert shape.
It will perhaps be as well to illustrate a few of the different brush strokes, and say something about the different qualities of each. These are only given as typical examples of the innumerable ways a brush may be used as an aid to very elementary students; every artist will, of course, develop ways of his own.
The touch will of necessity depend in the first instance upon the shape of the brush, and these shapes are innumerable. But there are two classes into which they can roughly be divided, flat and round. The round brushes usually sold, which we will call Class A, have rather a sharp point, and this, although helpful in certain circumstances, is against their general usefulness. But a round brush with a round point is also made, and this is much more convenient for mass drawing. Where there is a sharp point the central hairs are much longer, and consequently when the brush is drawn along and pressed so that all the hairs are touching the canvas, the pressure in the centre, where the long hairs are situated, is different from that at the sides. This has the effect of giving a touch that is not equal in quality all across, and the variety thus given is difficult to manipulate. I should therefore advise the student to try the blunt-ended round brushes first, as they give a 116much more even touch, and one much more suited to painting in planes of tone.
The most extreme flat brushes (Class B) are thin and rather short, with sharp square ends, and have been very popular with students. They can be relied upon to give a perfectly flat, even tone, but with a rather hard sharp edge at the sides, and also at the commencement of the touch. In fact, they make touches like little square bricks. But as the variety that can be got out of them is limited, and the amount of paint they can carry so small that only short strokes can be made, they are not the best brush for general use. They are at times, when great refinement and delicacy are wanted, very useful, but are, on the whole, poor tools for the draughtsman in paint. Some variety can be got by using one or other of their sharp corners, by which means the smallest possible touch can be made to begin with, which can be increased in size as more pressure is brought to bear, until the whole surface of the brush is brought into play. They are also often used to paint across the form, a manner illustrated in the second touch, columns 1 and 2 of the illustration on page 114 [Transcribers Note: Plate XXVI].
A more useful brush (Class C) partakes of the qualities of both flat and round. It is made with much more hair than the last, is longer, and has a square top with rounded corners. This brush carries plenty of paint, will lay an even tone, and, from the fact that the corners are rounded and the pressure consequently lessened at the sides, does not leave so hard an edge on either side of your stroke.
Another brush that has recently come into fashion is called a filbert shape (Class D) by the makers. It is a fine brush to draw with, as being 117flat it paints in planes, and having a rounded top is capable of getting in and out of a variety of contours. They vary in shape, some being more pointed than others. The blunt-ended form is the best for general use. Either this class of brush or Class C are perhaps the best for the exercises in mass drawing we have been describing. But Class A should also be tried, and even Class B, to find out which suits the particular individuality of the student.
On page 114 [Transcribers Note: Plate XXVI] a variety of touches have been made in turn by these different shaped brushes.
In all the strokes illustrated it is assumed that the brush is moderately full of paint of a consistency a little thinner than that usually put up by colourmen. To thin it, mix a little turpentine and linseed oil in equal parts with it; and get it into easy working consistency before beginning your work, so as not to need any medium.
In the first column (No. 1), a touch firmly painted with an equal pressure all along its course is given. This gives you a plane of tone with firm edges the width of your brush, getting gradually darker or lighter as your brush empties, according to the length of the stroke and to whether you are painting into a lighter or darker ground.
In column No. 2 a drag touch is illustrated. This is a very useful one. The brush is placed firmly on the canvas and then dragged from the point lightly away, leaving a gradated tone. A great deal of the modelling in round objects is to be expressed by this variety of handling. The danger is that its use is apt to lead to a too dexterous manner of painting; a dexterity more concerned with the clever manner in which a thing is painted than with the truth expressed.
118Column No. 3. This is a stroke lightly and quickly painted, where the brush just grazes the surface of the canvas. The paint is put on in a manner that is very brilliant, and at the same time of a soft quality. If the brush is only moderately full, such touches will not have any hard edges, but be of a light, feathery nature. It is a most useful manner of putting on paint when freshness of colour is wanted, as it prevents one tone being churned up with another and losing its purity. An............
